Are you curious about how GPS works? If so, you’re in luck! This article will explain the basics of GPS technology in a way that’s easy to understand.
GPS stands for Global Positioning System and it is a network of satellites that orbit the earth. These satellites transmit signals back to earth that can be used to determine one’s precise location. GPS receivers are able to pick up these signals and use them to calculate their location with great accuracy.
The most amazing thing about GPS is that it can be used anywhere in the world, and it doesn’t require any type of ground-based infrastructure.
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. The system is maintained by the United States government and is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver.
There are four main components of the GPS system: space segment, control segment, user segment, and ground station.
The space segment consists of 24 operational satellites (as of 2006) in six earth-orbiting planes. Each satellite circles the earth twice a day at about 12,000 miles (19,300 km) above the surface.
They transmit signals allowing a GPS receiver to determine its precise location on Earth.
The control segment consists of five monitoring stations located around the world that track the satellites and make sure they are working properly. They also keep accurate time data so that it can be synced up with atomic clocks on Earth.
Periodically, they upload new almanac data to the satellites so that receivers will have updated information about satellite positions.
The user segment is made up of all the people who use GPS receivers for various purposes such as navigation, surveying, mapping, timing events, etc. There are millions of users worldwide!
A ground station is not necessary for GPS operation but it can be used to improve accuracy in certain situations. Ground stations are usually located near large bodies of water because they reflect signals well and help create a “line-of-sight” path from satellite to receiver . A typical ground station has two antennas which receive signals from different satellites at different times; this allows for better triangulation and more accurate position determination .
Credit: trakkitgps.com
How Does Gps Work in Simple Terms?
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a satellite-based navigation system that consists of a network of 24 satellites placed into orbit by the U.S. Department of Defense. GPS receivers have antennas that receive signals from these satellites.
The satellite sends out a signal that includes the time and position information. This information is then processed by the receiver to calculate the user’s precise location.
How does GPS work in simple terms?
The basic principle behind GPS is really quite simple: it uses satellites orbiting overhead to help you determine your location on Earth. There are at least 24 GPS satellites in constant motion around our planet, beaming down signals from space (see How Satellites Work for details). Your GPS receiver picks up these signals, interprets them and triangulates your position — telling you where you are relative to those orbiting satellites (and, ultimately, telling you where you are on the face of the planet).
What is Gps Explained for Kids?
Since its inception in the 1970s, the Global Positioning System (GPS) has revolutionized the way we live and travel. This technology uses a network of satellites to provide accurate information about an object’s location on Earth.
GPS is used in a variety of ways, from guiding drivers to their destination to helping people find their way while hiking in the woods.
The military also relies on GPS for guidance when conducting operations.
How does GPS work?
Each GPS satellite transmits a signal that includes data about the satellite’s position and the current time.
A GPS receiver picks up these signals and uses them to calculate the satellite’s position. Once it has information from three or more satellites, the receiver can determine its own precise location.
Differential GPS is an even more accurate form of this technology that takes into account slight variations in satellite positions.
This system is often used by surveyors, who need very precise measurements for their work.
GPS has become an essential tool for modern life, and it shows no signs of slowing down!
How is Gps System Useful Short Answer?
GPS, or the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system that allows users to determine their precise location anywhere in the world. GPS can be used for a variety of purposes, including mapping and surveying, tracking movements of people or assets, and providing guidance for vehicles.
While GPS is most commonly associated with car navigation systems, it has a wide range of other applications as well.
For example, GPS can be used to track the movement of animals or to monitor the status of agricultural crops. It can also be used in search and rescue operations to locate missing persons.
One of the key benefits of GPS is its accuracy.
GPS signals are relatively weak and can be easily disrupted by factors like trees or buildings. However, by using multiple satellites and sophisticated algorithms, GPS receivers are able to triangulate their position with great accuracy.
Another advantage of GPS is its ubiquity.
Unlike other navigation systems that require specific infrastructure (like ground-based radio towers), GPS can be used anywhere in the world where there is an unobstructed view of the sky. This makes it an ideal solution for applications like air and marine navigation where traditional methods may not work well.
Overall, GPS provides a versatile and powerful tool for anyone who needs to know their exact location or track the movement of people or objects over time.
How Does Gps Find Your Location?
GPS is a technology that uses satellites to determine your location. The GPS system was originally developed for the military, but it is now available for civilian use.
GPS works by triangulation.
There are at least 24 GPS satellites orbiting the earth. Each satellite transmits a signal that includes its position and the time the signal was sent. Your GPS receiver picks up these signals from several satellites and uses them to calculate your exact location.
The GPS receiver needs line of sight to four or more satellites to work properly. This means that it needs an unobstructed view of the sky. If you are indoors or in a heavily wooded area, your GPS receiver may not be able to pick up enough signals to give you an accurate reading.
How GPS Works Today
How Gps Tracker Works
A GPS tracker is a device that uses the Global Positioning System to track the location of a person or object. The tracker sends out a signal that is picked up by satellites, which then calculate the position of the tracker and send this information back to the user.
There are a number of different GPS tracking devices available on the market, each with its own set of features.
Some devices are designed for use in vehicles, while others can be carried by an individual. There are also standalone devices that can be placed in a specific location, such as a car or room, to track the movements of someone within that area.
GPS tracking can be used for a variety of purposes, such as keeping track of children or elderly relatives, monitoring employees or assets, and even locating lost pets.
Gps Working Principle And Diagram
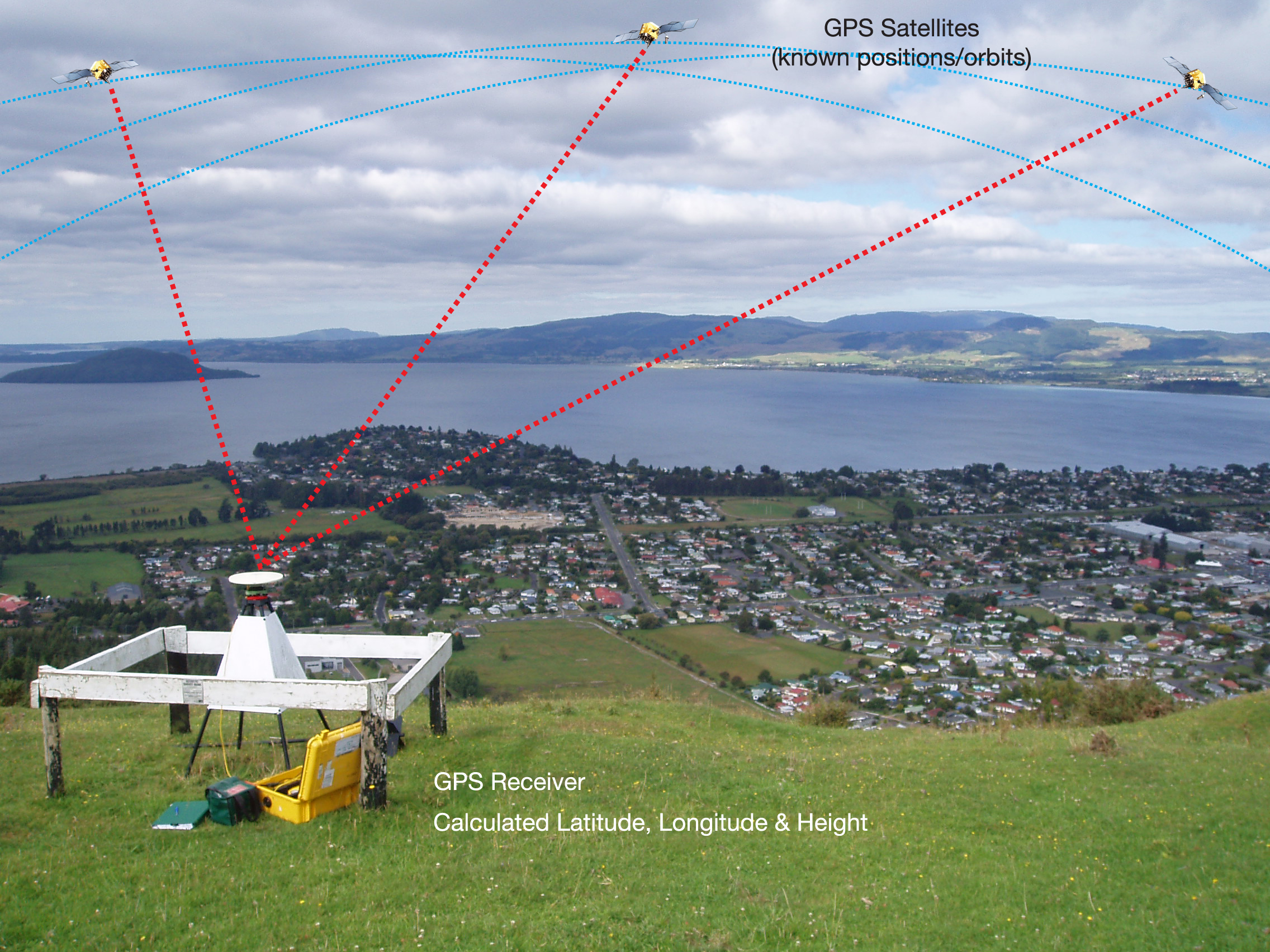
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a space-based satellite navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. The system is operated by the United States government and is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver.
A GPS receiver calculates its position by timing the signals sent by GPS satellites high above the Earth.
Each satellite continually broadcasts messages that include
the time the message was transmitted and the satellite position at that time. The receiver uses these messages to calculate its distance from each satellite.
This distance information, together with corrections for atmospheric effects, allows the receiver to calculate its three-dimensional position (latitude, longitude, and altitude) as well as the current local time.
GPS receivers come in a variety of form factors, including handheld units suitable for use while hiking, geocaching, surveying, boating or driving; mobile units mounted on vehicles; desktop units; and integrated circuit chips used in many consumer devices such as automotive navigation systems, personal digital assistants (PDAs), computers with mapping software and Smartphones. Some newer car models include factory-installed GPS receivers that are integrated into their audio or infotainment systems.
How Gps Works in Phone
GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a technology that allows us to pinpoint our exact location on the earth. It’s what allows us to use map apps on our phones and find our way around unfamiliar places. But how does GPS work?
GPS works by using a network of satellites that orbit the earth. These satellites send out signals that contain information about their location. GPS receivers, like the one in your phone, pick up these signals and use them to calculate your exact location.
Most GPS receivers can determine your position to within a few meters. That’s pretty amazing when you think about it! And it’s all thanks to those little satellites orbiting overhead.
How Gps Works Pdf
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a satellite-based navigation system that consists of 24 satellites, 3 control stations and a user unit. The GPS satellites orbit the earth in 12 hours at an altitude of 20,200 kilometers.
They transmit signals to the ground that can be picked up by GPS receivers.
The GPS receiver uses these signals to calculate its position relative to the satellites. ThePosition Location Information (PLI) service provides coordinates accurate to within 10 meters.
Once the receiver has calculated its position, it can provide information about nearby businesses, establishments and landmarks.
Conclusion
GPS stands for Global Positioning System and it is a network of satellites that orbit the Earth. GPS works by triangulation, which means it uses three or more satellite signals to pinpoint your location on the planet.
Each satellite in the GPS network broadcasts a signal that contains information about the satellite’s location and the current time.
When you turn on your GPS receiver, it starts searching for these signals. Once it finds three or more signals, it uses trilateration to calculate your exact location.
Trilateration is a math problem that gives you the distance from two points (in this case, satellites) and then lets you find a third point (your location) that is an equal distance from both points.
GPS receivers have very accurate clocks built into them so they can measure the time delay between when each signal was sent and when it was received. By knowing how far away each satellite is and using the time delay data, the GPS receiver can calculate your exact location on Earth.