Have you ever wondered how those little devices in your car or on your phone can tell you exactly where you are and how to get to your destination? It’s all thanks to satellite navigation, more commonly known as GPS. But how does GPS work?
Let’s take a closer look.
GPS stands for Global Positioning System and is a network of satellites that orbit the earth. There are at least 24 satellites in the GPS system, but there are usually 3-4 extra satellites in case one fails.
These satellites send out signals that contain information about their location and the current time.
Satellite navigation, or GPS, is a technology that allows you to determine your location on Earth using a network of satellites. GPS receivers use these satellites to calculate your position in three dimensions: latitude, longitude, and altitude.
GPS was originally developed for the military, but it has since become an essential tool for civilians as well.
Today, GPS is used in everything from navigation apps on our smartphones to tracking devices for cars and trucks.
How does GPS work?
Each GPS satellite transmits a signal that includes information about the satellite’s current position and the precise time the signal was sent.
A GPS receiver uses this information to calculate its own position relative to the satellite. By measuring the distance between itself and at least four satellites, a GPS receiver can determine its latitude, longitude, and altitude with great accuracy.
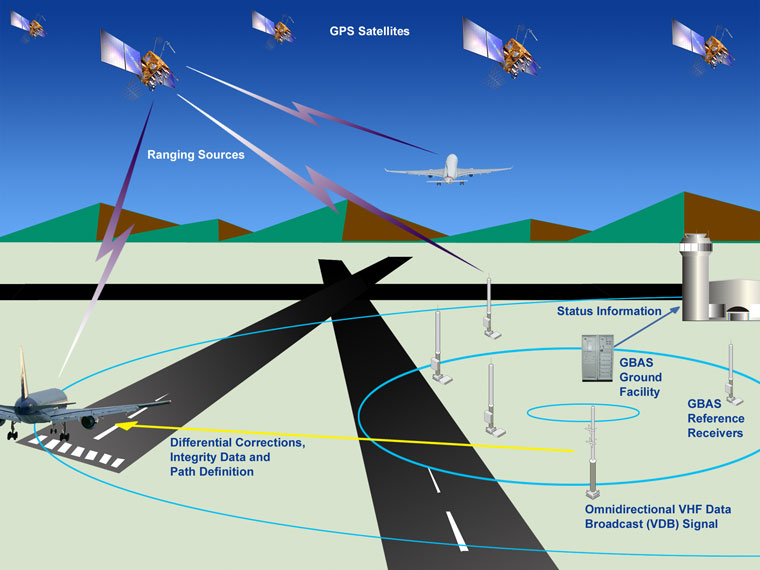
Credit: www.faa.gov
How Does a Satellite. Gps Work?
A satellite GPS system uses a constellation of 24+ satellites that are in orbit around the Earth. These satellites transmit signals that allow GPS receivers to determine their precise location on Earth. How does this work?
The basic principle behind satellite-based positioning is triangulation, or the process of determining one’s location by measuring angles to nearby objects. In the case of GPS, the “objects” are satellites, and the measurements are made by timing how long it takes for a signal from each satellite to reach a receiver here on Earth. By knowing the precise locations of three or more satellites, and timing how long it took for their signals to reach your GPS receiver, your receiver can calculate its own position on Earth with great accuracy.
GPS receivers use this information to provide you with real-time data on your current position, speed, and heading. They can also be used to plot routes and track your progress as you travel. And because GPS signals are transmitted continuously from every satellite in the constellation, you can always get up-to-date information on your location no matter where you are in the world.
How Do Gps Connect to Satellites?
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a satellite-based navigation system that consists of a network of 24 satellites placed into orbit by the U.S. Department of Defense. These satellites are constantly sending out signals that contain information about their location and the current time.
GPS receivers use these signals to calculate the receiver’s exact location and the current time.
The first thing a GPS receiver does is acquire the signal from at least four satellites. The receiver then uses this information to calculate its position in three dimensions: latitude, longitude, and altitude.
Once the initial position has been calculated, the GPS receiver can continue to track its position even if it moves around or loses sight of some of the satellites. This is because each satellite transmits information about its own location as well as the locations of all other visible satellites. By tracking multiple satellites, the GPS receiver can triangulate its own position very accurately.
GPS technology has become essential for many applications including mapping, surveying, navigation, timing, and more recently location-based services (LBS). LBS applications use GPS to provide users with up-to-date information on businesses and services in their vicinity (e.g., restaurants, gas stations, ATMs).
Can Gps Work Without Internet?
Yes, GPS can work without an internet connection. The Global Positioning System is a satellite-based navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth’s surface. There are 24 satellites in the GPS constellation, which orbits about 12,550 miles (20,200 kilometers) above the Earth.
Each satellite transmits data that allows a GPS receiver on the ground to calculate its precise location.
GPS receivers use this information to determine their current position, velocity and time relative to other locations on Earth. A GPS receiver needs four or more of these satellites to be visible in order to calculate its position with any degree of accuracy.
If a receiver has a clear view of six or more satellites, it can usually determine its three-dimensionalposition (latitude, longitude and altitude) as well as the current local time accurate to within a few milliseconds.
In general, you need an unobstructed view of the sky for GPS to work properly. However, there are now handheld devices available that use both GPS and GLONASS (the Russian equivalent of GPS) constellations and can switch between them if one system is not working properly due to bad weather or some other obstruction.
How Does a Gps Receiver Know Where a Gps Satellite Is?
A GPS receiver needs four satellites to calculate its position in three dimensions. It calculates the distance to each satellite using the travel time of radio waves. The receiver compares the known position of each satellite with its calculated distance from the receiver.
This comparison reveals where the satellites are relative to the receiver, and from that information, the GPS can deduce its own location.
Satellite Navigation – GPS – How It Works
How Gps Tracker Works
GPS trackers are devices that use the Global Positioning System to determine the precise location of a vehicle, person, or other asset to which it is attached. GPS tracking devices relay this information via satellite to a designated recipient in real-time. This technology can be used for a variety of purposes, such as monitoring the whereabouts of fleet vehicles or keeping tabs on high-value assets.
How do GPS trackers work?
A GPS tracker contains a SIM card that connects it to the cellular network. Once activated, the tracker begins transmitting its coordinates to a designated server via text message (SMS).
The server then processes this information and makes it available to authorized users in near-real-time. Some GPS trackers also come equipped with additional features like geofencing and live tracking. Geofencing allows users to set up virtual boundaries around specific locations; if the tracker crosses one of these boundaries, an alert is generated.
Live tracking lets authorized users see the current location of the tracker on a map in near-real-time.
GPS trackers are an effective way to keep tabs on people, vehicles, and assets. However, it’s important to note that they only work if there’s an active cellular connection – if there’s no service, the tracker will not be able send its coordinates.
Additionally, while most trackers are designed for use indoors and outdoors, some models may not be accurate when used in certain environments (e.g., underground parking garages).
How Gps Works Step-By-Step
GPS is a technology that has revolutionized the way we live and travel. It’s hard to imagine living without it, but there are still many people who don’t know how GPS works. In this blog post, we’re going to explain exactly how GPS works, step-by-step.
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It is a satellite-based navigation system that consists of a network of 24 satellites orbiting the earth, as well as a ground control station and user equipment. The satellites transmit signals to the user equipment, which then uses these signals to calculate its position on Earth.
The first step in understanding how GPS works is to understand how the satellite signal is transmitted and received. Each satellite in the GPS constellation transmits a signal that contains information about its location and time. This signal is picked up by the user equipment, which then uses it to calculate its distance from the satellite.
Once it has calculated its distance from four or more satellites, it can determine its location on Earth with great accuracy.
Now let’s take a look at how this process works in more detail:
1) The satellite transmits a signal that contains information about its location and time;
2) The user equipment picks up this signal; 3) Using the information contained in the signal, it calculates its distance from the satellite; 4) Once it has calculated its distance from four or more satellites (known as “trilateration”), it can determine its location on Earth with great accuracy; 5) The user equipment can then use this information to provide turn-by-turn directions, show your current location on a map, or track your progress while traveling.
How Gps Works in Phone
GPS systems have been a staple in phones for years, but how do they work? Let’s take a look at how GPS works in phones and how it can be used to your advantage.
GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation system that consists of 24 satellites that orbit the earth.
These satellites transmit signals that allow GPS receivers to calculate their exact location. GPS receivers are found in everything from cars to phones to fitness trackers.
Most smartphones come with built-in GPS receivers these days.
When you open up your phone’s maps app, it uses your phone’s GPS receiver to pinpoint your location on the map. That way, you can see exactly where you are and get directions to where you want to go.
GPS can also be used for other things besides just getting directions.
For example, many running apps use GPS to track your route and distance traveled. And if you have a fitness tracker with GPS, it can be used to track your steps, calories burned, and more.
Overall, GPS is a handy tool that can be used in a variety of ways.
If you have a smartphone with built-in GPS, be sure to take advantage of all its features!
How Gps Works Pdf
GPS is a system that uses satellites to provide accurate location information. It can be used for a variety of purposes, including navigation, tracking, and mapping.
The basic principle behind GPS is simple.
A network of satellites orbit the earth, transmitting signals back to earth. GPS receivers pick up these signals and use them to calculate the receiver’s location. The more satellites a receiver can pick up, the more accurate the location information will be.
There are four main components to the GPS system: space segment, control segment, user segment, and applications segment.
The space segment consists of a constellation of 24 satellites that orbit the earth at an altitude of 20,000 kilometers (12,500 miles). The satellites are distributed evenly in six orbital planes so that there are always at least four visible from any point on earth at any time.
Each satellite has atomic clocks onboard to keep precise time.
The control segment consists of ground stations located around the world that track the GPS satellites and make sure they are operating properly. The data from the tracking stations is used to calculate the orbits of the satellites and make corrections as needed.
This data is then transmitted back to the satellites so they can broadcast their correct position information.
The user segment consists of GPS receivers that pick up signals from GPS satellites and use them to calculate location information. There are two types of receivers: stand-alone units that are used for navigation or tracking purposes; and integrated units that are built into other devices such as cell phones or automobiles.
Conclusion
Satellite navigation, or GPS, is a technology that allows users to determine their precise location on Earth. GPS works by triangulating the user’s position relative to a network of satellites in orbit around the planet. By measuring the distance to several satellites, the GPS receiver can calculate its exact location.
GPS has become an essential tool for navigation, both on land and at sea. It is widely used by hikers and mountaineers to find their way in unfamiliar terrain, and by boaters and pilots to chart a safe course through treacherous waters. GPS is also playing an increasingly important role in transportation, as more and more vehicles are equipped with satellite-based navigation systems.